- Atomic Mass Of Naclo3
- Atomic Mass Of Naclo
- Atomic Mass Of Naclo
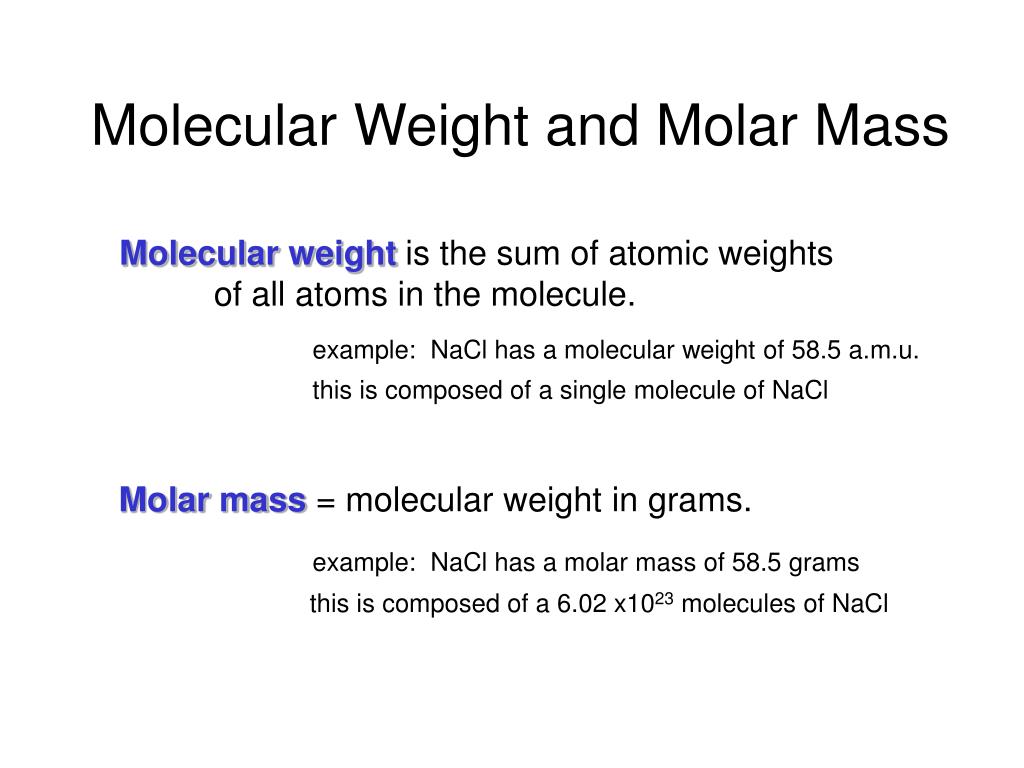
- Formula Mass Of Nacl
- Finding Mass Of Solute
Learning Objectives
- To determine the formula mass of an ionic or molecular compound.
Thus, since the atomic mass of iron is 55.847 amu, one mole of iron atoms would weigh 55.847 grams. The same concept can be extended to ionic compounds and molecules. One formula unit of sodium chloride (NaCl) would weigh 58.44 amu (22.98977 amu for Na + 35.453 amu for Cl), so a mole of sodium chloride would weigh 58.44 grams. For example, the molar mass of NaCl can be calculated for finding the atomic mass of sodium (22.99 g/mol) and the atomic mass of chlorine (35.45 g/mol) and combining them. 0.0 (0 votes) Log in to add comment. Sodium chloride / ˌsoʊdiəm ˈklɔːraɪd /, commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g/mol respectively, 100 g of NaCl contains 39.34 g Na and 60.66 g Cl. The molar mass of sodium is 22.990 g/mol. The molar mass of chlorine is 35.45 g/mol. To calculate the molar mass of NaCl, multiply the subscript of each element times its molar mass, then add them together. If there is no subscript, it is understood to be 1. A mol of 12 C atoms has a mass 12 g: the molar mass of 12 C is 12 g A mol of Cl 2 molecules has a mass 70.90 g: the molar mass of Cl 2 is 70.90 g A mol of NaCl has a mass 58.5 g: the molar mass of NaCl is 58.5 g If we revisit the reaction between magnesium and chlorine, Mg(s) + Cl 2 (g) - MgCl 2 (s).
A necessary skill for future chapters is the ability to determine the mass of the formula of an ionic compound. This quantity is called the formula mass. The formula mass is obtained by adding the masses of each individual atom in the formula of the compound. Because a proper formula is electrically neutral (with no net electrons gained or lost), the ions can be considered atoms for the purpose of calculating the formula mass.
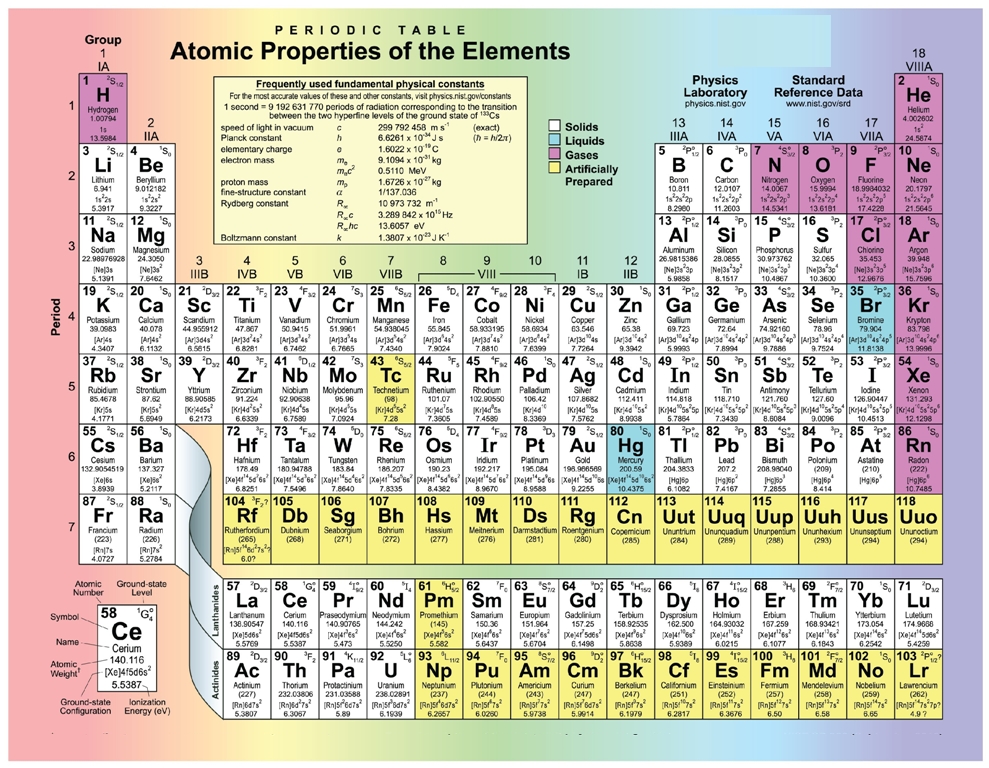
Let us start by calculating the formula mass of sodium chloride (NaCl). This formula mass is the sum of the atomic masses of one sodium atom and one chlorine atom, which we find from the periodic table; here, we use the masses to two decimal places:
Na: 22.99 amu
Cl: +35.34 amu
Total: 58.44 amu
To two decimal places, the formula mass of NaCl is 58.44 amu.
When an ionic compound has more than one anion or cation, you must remember to use the proper multiple of the atomic mass for the element in question. For the formula mass of calcium fluoride (CaF2), we must multiply the mass of the fluorine atom by 2 to account for the two fluorine atoms in the chemical formula:
Ca: 1 x 40.08 = 40.08 amu
F: 2 x 19.00 = +38.00 amu
Total = 78.08 amu
The formula mass of CaF2 is 78.08 amu.
For ionic compounds with polyatomic ions, the sum must include the number and mass of each atom in the formula for the polyatomic ion. For example, potassium nitrate (KNO3) has one potassium atom, one nitrogen atom, and three oxygen atoms:
K: 1 x 39.10 = 39.10 amu
N: 1 x 14.00 = +14.00 amu
O: 3 x 16.00 = +48.00 amu
Total = 101.10 amu
The formula mass of KNO3 is 101.10 amu.
Potassium nitrate is a key ingredient in gunpowder and has been used clinically as a diuretic.
When a formula contains more than one polyatomic unit in the chemical formula, as in Ca(NO3)2, do not forget to multiply the atomic mass of every atom inside of the parentheses by the subscript outside of the parentheses. This is necessary because the subscript refers to the entire polyatomic ion. Thus, for Ca(NO3)2, the subscript 2 implies two complete nitrate ions, so we must sum the masses of two (1 × 2) nitrogen atoms and six (3 × 2) oxygen atoms, along with the mass of a single calcium atom:
Ca: 1 x 40.08 = 40.08 amu
N: 2 x 14.00 = +28.00 amu
O: 6 x 16.00 = +96.00 amu
Total = 164.08 amu
The key to calculating the formula mass of an ionic compound is to correctly count each atom in the formula and multiply the atomic masses of its atoms accordingly.
Example (PageIndex{1})
Use the atomic masses (rounded to two decimal places) to determine the formula mass for each ionic compound.
- FeCl3
- (NH4)3PO4
Solution
a.
Fe: 1 x 55.85 = 55.85 amu
Cl: 1 x 35.45 = +106.35 amu
________________________
Total = 162.20 amu
The formula mass of FeCl3 is 162.2 amu.
b. When we distribute the subscript 3 through the parentheses containing the formula for the ammonium ion, we see that we have 3 nitrogen atoms and 12 hydrogen atoms. Thus, we set up the sum as follows:
N: 3 x 14.00 = 42.00 amu
H: 12 x 1.00 = +12.00 amu
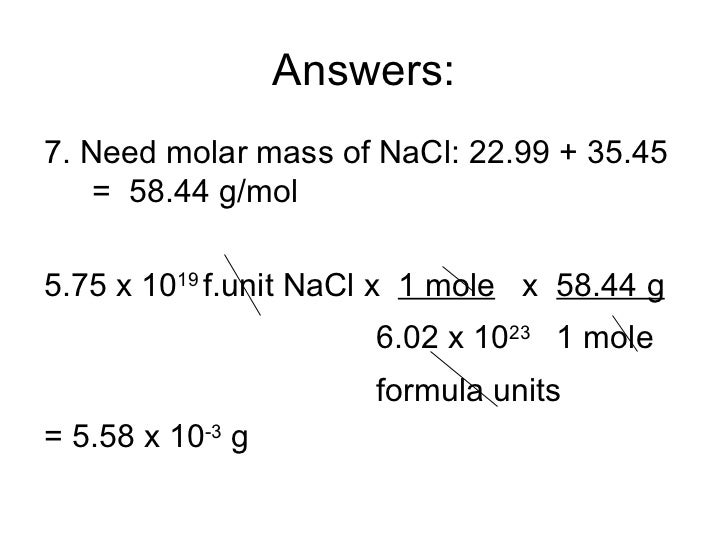
P: 1 x 30.97 = +30.97 amu
O: 4 x 16.00 = +64.00 amu
Total = 148.97 amu
The formula mass for (NH4)3PO4 is 149.0 amu.
Exercise (PageIndex{1})
Use the atomic masses (rounded to two decimal places) to determine the formula mass for each ionic compound.
- TiO2
- AgBr
- Au(NO3)3
- Fe3(PO4)2
Answer
a. 79.87 amu
b. 187.77 amu
c. 383.0 amu
To Your Health: Hydrates
Some ionic compounds have water (H2O) incorporated within their formula unit. These compounds, called hydrates, have a characteristic number of water units associated with each formula unit of the compound. Hydrates are solids, not liquids or solutions, despite the water they contain.
To write the chemical formula of a hydrate, write the number of water units per formula unit of compound after its chemical formula. The two chemical formulas are separated by a vertically centered dot. The hydrate of copper(II) sulfate has five water units associated with each formula unit, so it is written as CuSO4•5H2O. The name of this compound is copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate, with the penta- prefix indicating the presence of five water units per formula unit of copper(II) sulfate.
Hydrates have various uses in the health industry. Calcium sulfate hemihydrate (CaSO4•½H2O), known as plaster of Paris, is used to make casts for broken bones. Epsom salt (MgSO4•7H2O) is used as a bathing salt and a laxative. Aluminum chloride hexahydrate is an active ingredient in antiperspirants. The accompanying table lists some useful hydrates.
| Formula | Name | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| AlCl3•6H2O | aluminum chloride hexahydrate | antiperspirant |
| CaSO4•½H2O | calcium sulfate hemihydrate (plaster of Paris) | casts (for broken bones and castings) |
| CaSO4•2H2O | calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum) | drywall component |
| CoCl2•6H2O | cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate | drying agent, humidity indicator |
| CuSO4•5H2O | copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate | fungicide, algicide, herbicide |
| MgSO4•7H2O | magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (Epsom salts) | laxative, bathing salt |
| Na2CO3•10H2O | sodium carbonate decahydrate (washing soda) | laundry additive/cleaner |
Key Takeaway
- Formula masses of ionic compounds can be determined from the masses of the atoms in their formulas.
Contributors and Attributions
Anonymous
Marisa Alviar-Agnew (Sacramento City College)
Henry Agnew (UC Davis)
6.2 Atomic and Molar Masses
Learning Objective
- Learn how the masses of moles of atoms and molecules are expressed.
Now that we have introduced the mole and practiced using it as a conversion factor, we ask the obvious question: why is the mole that particular number of things? Why is it 6.022 × 1023 and not 1 × 1023 or even 1 × 1020?
The number in a mole, Avogadro’s number, is related to the relative sizes of the atomic mass unit and gram mass units. Whereas one hydrogen atom has a mass of approximately 1 u, 1 mol of H atoms has a mass of approximately 1 gram. And whereas one sodium atom has an approximate mass of 23 u, 1 mol of Na atoms has an approximate mass of 23 grams.
One mole of a substance has the same mass in grams that one atom or molecule has in atomic mass units. The numbers in the periodic table that we identified as the atomic masses of the atoms not only tell us the mass of one atom in u but also tell us the mass of 1 mol of atoms in grams.
Note
One mole of a substance has the same mass in grams that one atom or molecule has in atomic mass units.
Example 3
What is the mass of each quantity?
- 1 mol of Al atoms
- 2 mol of U atoms
Solution
- One mole of Al atoms has a mass in grams that is numerically equivalent to the atomic mass of aluminum. The periodic table shows that the atomic mass (rounded to two decimal points) of Al is 26.98, so 1 mol of Al atoms has a mass of 26.98 g.
- According to the periodic table, 1 mol of U has a mass of 238.03 g, so the mass of 2 mol is twice that, or 476.06 g.
Skill-Building Exercise
5 mol of Br atoms
What is the mass of each quantity?
The mole concept can be extended to masses of formula units and molecules as well. The mass of 1 mol of molecules (or formula units) in grams is numerically equivalent to the mass of one molecule (or formula unit) in atomic mass units. For example, a single molecule of O2 has a mass of 32.00 u, and 1 mol of O2 molecules has a mass of 32.00 g. As with atomic mass unit–based masses, to obtain the mass of 1 mol of a substance, we simply sum the masses of the individual atoms in the formula of that substance. The mass of 1 mol of a substance is referred to as its molar massThe mass of 1 mol of atoms or molecules., whether the substance is an element, an ionic compound, or a covalent compound.
Example 4
What is the mass of 1 mol of each substance?
Atomic Mass Of Naclo3
- NaCl
- bilirubin (C33H36N4O6), the principal pigment present in bile (a liver secretion)
Atomic Mass Of Naclo
Solution
Summing the molar masses of the atoms in the NaCl formula unit gives
1 Na molar mass: 23.00 g 1 Cl molar mass: 35.45 g Total: 58.45 g The mass of 1 mol of NaCl is 58.45 g.
Multiplying the molar mass of each atom by the number of atoms of that type in bilirubin’s formula and adding the results, we get
33 C molar mass: 33 × 12.01 g 396.33 g 36 H molar mass: 36 × 1.01 = 36.36 g 4 N molar mass: 4 × 14.00 = 56.00 g 6 O molar mass: 6 × 16.00 = 96.00 g Total: 584.69 g The mass of 1 mol of bilirubin is 584.69 g.
Atomic Mass Of Naclo
Skill-Building Exercise
barium sulfate (BaSO4), used to take X rays of the gastrointestional tract
adenosine (C10H13N5O4), a component of cell nuclei crucial for cell division
What is the mass of 1 mol of each substance?
Be careful when counting atoms. In formulas with polyatomic ions in parentheses, the subscript outside the parentheses is applied to every atom inside the parentheses. For example, the molar mass of Ba(OH)2 requires the sum of 1 mass of Ba, 2 masses of O, and 2 masses of H:
| 1 Ba molar mass: | 1 × 137.33 g = | 137.33 g |
| 2 O molar mass: | 2 × 16.00 g = | 32.00 g |
| 2 H molar mass: | 2 × 1.01 g = | 2.02 g |
| Total: | 171.35 g |
Because molar mass is defined as the mass for 1 mol of a substance, we can refer to molar mass as grams per mole (g/mol). The division sign (/) implies “per,” and “1” is implied in the denominator. Thus, the molar mass of bilirubin can be expressed as 584.05 g/mol, which is read as “five hundred eighty four point zero five grams per mole.”
Concept Review Exercises
How are molar masses of compounds determined?
Formula Mass Of Nacl
Answers
Molar masses of the elements are the same numeric value as the masses of a single atom in atomic mass units but in units of grams instead.
Molar masses of compounds are calculated by adding the molar masses of their atoms.
Key Takeaway
Finding Mass Of Solute
- The mass of moles of atoms and molecules is expressed in units of grams.
Exercises
What is the molar mass of Si? What is the molar mass of U?
What is the molar mass of Mn? What is the molar mass of Mg?
What is the molar mass of FeCl2? What is the molar mass of FeCl3?
What is the molar mass of C6H6? What is the molar mass of C6H5CH3?
What is the molar mass of (NH4)2S? What is the molar mass of Ca(OH)2?
What is the molar mass of (NH4)3PO4? What is the molar mass of Sr(HCO3)2?
Aspirin (C9H8O4) is an analgesic (painkiller) and antipyretic (fever reducer). What is the molar mass of aspirin?
Ibuprofen (C13H18O2) is an analgesic (painkiller). What is the molar mass of ibuprofen?
Morphine (C17H19NO3) is a narcotic painkiller. What is the mass of 1 mol of morphine?
Heroin (C21H23NO5) is a narcotic drug that is a derivative of morphine. What is the mass of 1 mol of heroin?
Answers
